Diagnostic Medical Ultrasound Technology
Who are Sonographers?
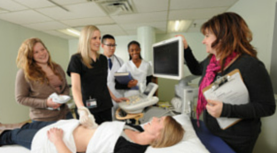 Sonographers are highly skilled health care professionals who use ultrasound (sound waves) to look inside a patient's body, evaluate the condition of various organs and record digital pictures.
Sonographers are highly skilled health care professionals who use ultrasound (sound waves) to look inside a patient's body, evaluate the condition of various organs and record digital pictures.
Sonographers evaluate organs and structures such as the liver, kidneys, heart, thyroid, blood vessels, muscles, ovaries and developing babies. Sonographers provide a summary of what they've discovered and discuss their findings with specialized doctors, who use this information to make a diagnosis.
Where do Sonographers work?
Sonographers usually work in hospitals or clinics, however some Sonographers work as managers, educators, equipment sales representatives, equipment applications specialists, medical information technology (IT) specialists or researchers.
How do I become a Sonographer?
The School of Health Sciences offers a four year Bachelor of Health Science (BHSc) degree program, which includes theory and practice. Students will take core professional development courses with a concentration on ultrasound specific knowledge and skills. A diploma option is possible after completion of Year 3.Ìý The program curriculum offers the necessary competencies to challenge the Sonography Canada professional examinations.
Entrance requirements
To be considered for admission High School applicants require grade 12 academic English, Math, Physics and Biology with no mark below 70% in each of these courses and an overall minimum average of 75%. Post secondary applicants require a minimum GPA of 2.75 (on a 4.30 scale), with no grade lower than C in prerequisite courses. PriorityÌýconsideration is given to permanent residents of the Maritime provinces, then to residents across Canada and then to all other applicants. Admission can be competitive and meeting the minimum entrance requirements does not guarantee admission.
Examples of courses in the program
- Human Anatomy & Physiology
- Pathophysiology for Health Sciences
- Sonography in Obstetrics
- Sonography of the Abdomen and Superficial Structures
- Health Care Ethics
- Foundations in Health Care Practice
- Statistics
- Digital Imaging
- Introduction to Health Research
Program outline
| View the course descriptions for Diagnostic Medical UltrasoundÌýTechnologyÌý» |
|---|
Certificate Options
| See certificate options in Cardiac Ultrasound and Vascular Ultrasound » |
|---|
Clinical Rotations
One of the benefits of studying at the School of Health Sciences is the opportunity to do hands-on clinical work. In years 1, 2, and 3, every student spends 6-8 weeks during the summer term completing a clinical practicum in a healthcare setting. In addition, third year students complete multiple clinical education courses directly in the clinical environment to help prepare them for entry to practice.
Most students complete their practicums across Atlantic Canada, while others may travel to locations across the country. Placement opportunities are based on clinical site availability and are subject to change from year to year. Health Sciences students are provided with more information about availability and options before each clinical experience.
Accreditation
Accreditation Canada is the program's accrediting body. For more information go to to view the list of accredited diagnostic medical ultrasound (sonography) programs.
Professional associations
Sonography Canada is the national professional body for Sonographers. Membership with the Sonography Canada is maintained through active registration with Sonography Canada and/or the American Registry of Diagnostic Medical Sonographers (ARDMS) and the Nova Scotia College of Medical Imaging and RadiationTherapy Professionals (NSCMIRTP). Registrants must undergo continuing professional development to maintain active registration.
Job opportunities
Sonographers are in high demand locally as well as throughout Canada and the United States. The working hours and salaries vary depending on the work setting and employer. Sonographers may be required to work or be on call over evenings, weekends or holidays. Starting salaries are comparable with other health science professionals.
For more information on Diagnostic Medical Ultrasound, please visit , , , or .
Ìý
Ìý
